Understanding Kube-OVN CNI
This document describes the general architecture of Kube-OVN, the functionality of each component and how they interact with each other.
Overall, Kube-OVN serves as a bridge between Kubernetes and OVN, combining proven SDN with Cloud Native. This means that Kube-OVN not only implements network specifications under Kubernetes, such as CNI, Service and Networkpolicy, but also brings a large number of SDN domain capabilities to cloud-native, such as logical switches, logical routers, VPCs, gateways, QoS, ACLs and traffic mirroring.
Kube-OVN also maintains a good openness to integrate with many technology solutions, such as Cilium, Submariner, Prometheus, KubeVirt, etc.
The components of Kube-OVN can be broadly divided into three categories.
- Upstream OVN/OVS components.
- Core Controller and Agent.
- Monitoring, operation and maintenance tools and extension components.
TOC
Upstream OVN/OVS Components
This type of component comes from the OVN/OVS community with specific modifications for Kube-OVN usage scenarios. OVN/OVS itself is a mature SDN system for managing virtual machines and containers, and we strongly recommend that users interested in the Kube-OVN implementation read ovn-architecture(7) first to understand what OVN is and how to integrate with it. Kube-OVN uses the northbound interface of OVN to create and coordinate virtual networks and map the network concepts into Kubernetes.
All OVN/OVS-related components have been packaged into images and are ready to run in Kubernetes.
ovn-central
The ovn-central Deployment runs the control plane components of OVN, including ovn-nb, ovn-sb, and ovn-northd.
ovn-nb: Saves the virtual network configuration and provides an API for virtual network management.kube-ovn-controllerwill mainly interact withovn-nbto configure the virtual network.ovn-sb: Holds the logical flow table generated from the logical network ofovn-nb, as well as the actual physical network state of each node.ovn-northd: translates the virtual network ofovn-nbinto a logical flow table inovn-sb.
Multiple instances of ovn-central will synchronize data via the Raft protocol to ensure high availability.
ovs-ovn
ovs-ovn runs as a DaemonSet on each node, with openvswitch, ovsdb, and ovn-controller running inside the Pod.
These components act as agents for ovn-central to translate logical flow tables into real network configurations.
Core Controller and Agent
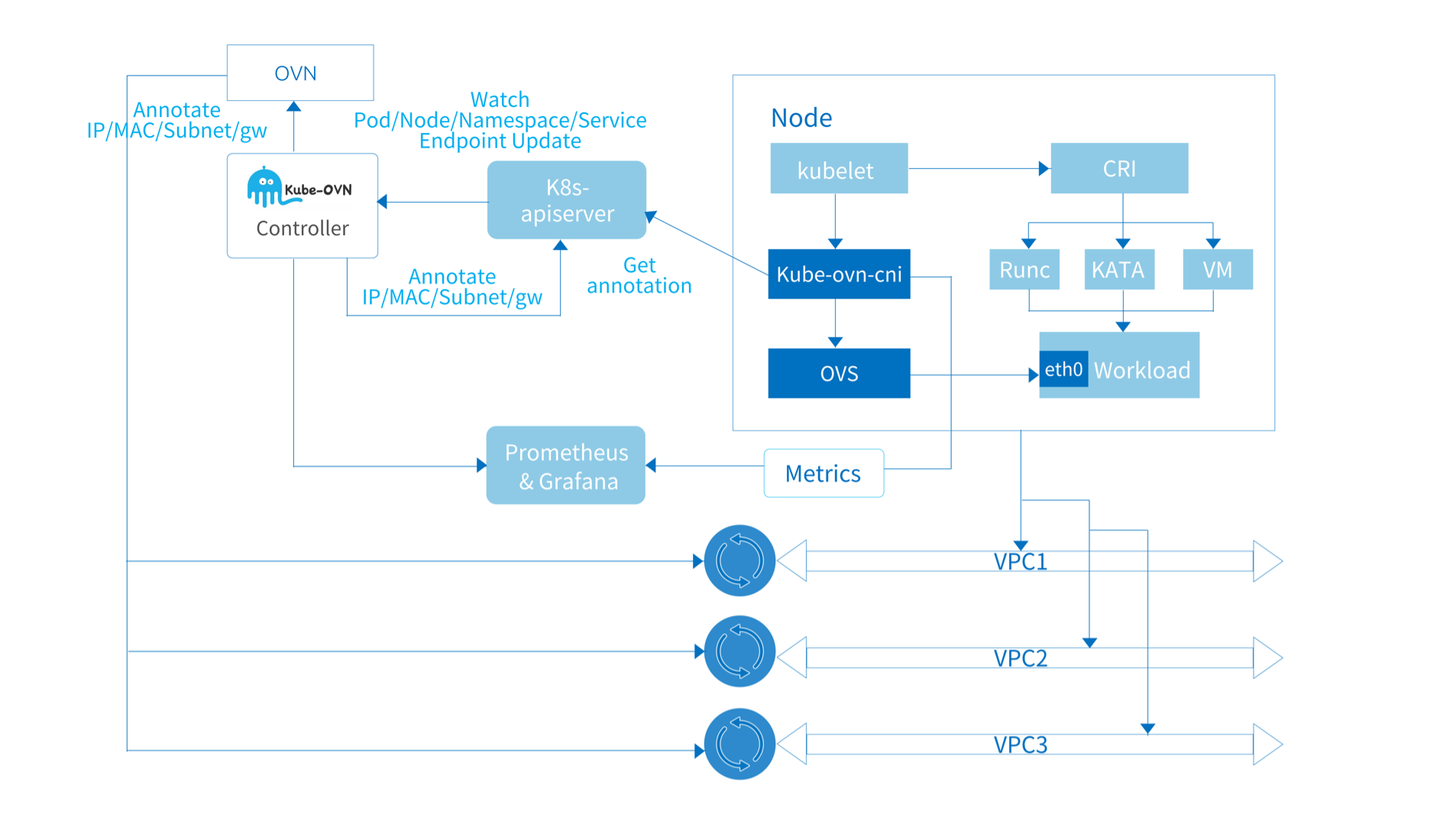
This part is the core component of Kube-OVN, serving as a bridge between OVN and Kubernetes, bridging the two systems and translating network concepts between them. Most of the core functions are implemented in these components.
kube-ovn-controller
This component performs the translation of all resources within Kubernetes to OVN resources and acts as the control plane for the entire Kube-OVN system.
The kube-ovn-controller listens for events on all resources related to network functionality and updates the logical network
within the OVN based on resource changes. The main resources listened including:
Pod, Service, Endpoint, Node, NetworkPolicy, VPC, Subnet, Vlan, ProviderNetwork.
Taking the Pod event as an example, kube-ovn-controller listens to the Pod creation event, allocates the address via the built-in in-memory IPAM function,
and calls ovn-central to create logical ports, static routes and possible ACL rules.
Next, kube-ovn-controller writes the assigned address and subnet information such as CIDR, gateway, route, etc. to the annotation of the Pod.
This annotation is then read by kube-ovn-cni and used to configure the local network.
kube-ovn-cni
This component runs on each node as a DaemonSet, implements the CNI interface, and operates the local OVS to configure the local network.
This DaemonSet copies the kube-ovn binary to each machine as a tool for interaction between kubelet and kube-ovn-cni.
This binary sends the corresponding CNI request to kube-ovn-cni for further operation.
The binary will be copied to the /opt/cni/bin directory by default.
kube-ovn-cni will configure the specific network to perform the appropriate traffic operations,
and the main tasks including:
- Config
ovn-controllerandvswitchd. - Handle CNI Add/Del requests:
- Create or delete veth pair and bind or unbind to OVS ports.
- Configure OVS ports
- Update host iptables/ipset/route rules.
- Dynamically update the network QoS.
- Create and configure the
ovn0NIC to connect the container network and the host network. - Configure the host NIC to implement Vlan/Underlay/EIP.
- Dynamically config inter-cluster gateways.
Monitoring, Operation and Maintenance Tools and Extension Components
These components provide monitoring, diagnostics, operations tools, and external interface to extend the core network capabilities of Kube-OVN and simplify daily operations and maintenance.
kube-ovn-speaker
This component is a DaemonSet running on a specific labeled nodes that publish routes to the external, allowing external access to the container directly through the Pod IP.
kube-ovn-pinger
This component is a DaemonSet running on each node to collect OVS status information, node network quality, network latency, etc.
kube-ovn-monitor
This component collects OVN status information and the monitoring metrics.
kubectl-ko
This component is a kubectl plugin, which can quickly run common operations.